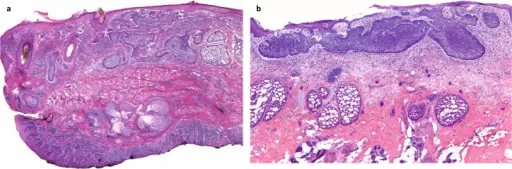
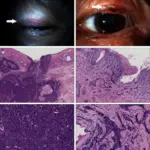
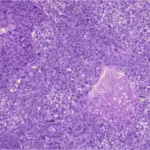
Basal cell carcinoma is a malignant epidermal tumor that affects the basement membrane of epithelial cells.
What is the Pathology of Basal Cell Carcinoma?
The pathology of basal cell carcinoma is Forms strands, cords and island of tumor appearing similar to the normal epithelial basal layer.
How does Basal Cell Carcinoma Present?
Basal cell carcinoma presents with Pearly appearance, crusting, telangiectasia, erosion or ulceration.
How is Basal Cell Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Basal cell carcinoma is diagnosed by assessment of ocular motility, assessment for proptosis, assessment of madarosis, assessment of eyelid malposition, incisional or excisional tissue biopsy.
How is Basal Cell Carcinoma Treated?
Basal cell carcinoma is treated with administration of Vismodegib, topical imiquimod 5% cream, surgical excision, sonidegib, intron-A, efudex, tazarotene, PD1-inhibitor.
What is the Prognosis of Basal Cell Carcinoma?
The prognosis of basal cell carcinoma is a 5 years cure rate. Prognosis gets worse with deeply invasive tumors, inadequate treatment, long-standing lesions, lesions greater than 3 cm.