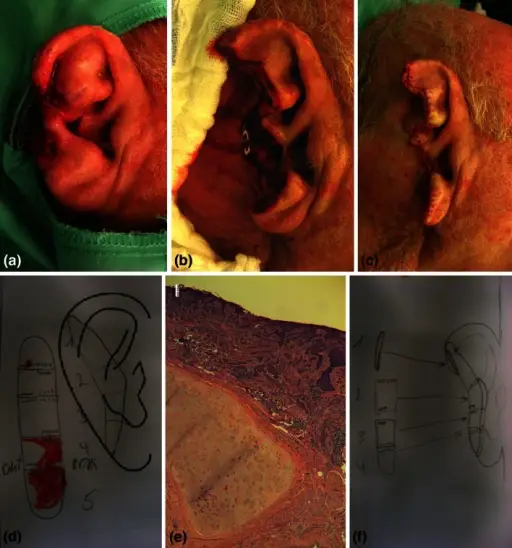
Basal cell carcinoma of the ear is a nest of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading associated with a fibromyxoid stroma.
What is the Pathology of Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Ear?
The pathology of basal cell carcinoma of the ear is:
-Etiology: The cause of basal cell carcinoma of the ear is typically UV radiation.
-Genes involved: TP53, PTCH1, SMO, CDKN2A, RAS.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to basal cell carcinoma of the ear is UV radiation induced carcinogenesis, mutations in TP53 gene, PTCH1 gene mutations, and activating mutations in SMO gene and other genes including mutations in the CDKN2A gene and RAS genes.
-Histology: The histology associated with basal cell carcinoma of the ear shows basophilic palisading groups of cells.
How does Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Ear Present?
Patients with basal cell carcinoma of the ear typically are male present at the age range of middle aged adults with increasing incidence with age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with basal cell carcinoma of the ear include a nodular variant that usually presents as a pearly pink or flesh colored papule or nodule with arborizing and branching vessels. The borders of basal cell carcinomas are typically rolled.
How is Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Ear Diagnosed?
Basal cell carcinoma of the ear is diagnosed by clinical features, dermatoscopy, and histological features.
How is Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Ear Treated?
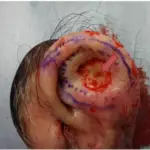
Basal cell carcinoma of the ear is treated by surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Ear?
The prognosis of basal cell carcinoma of the ear is fair.