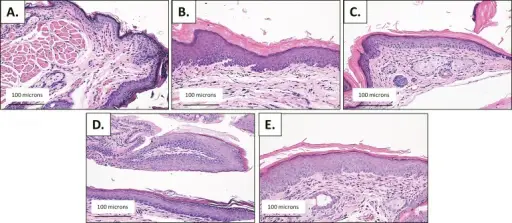
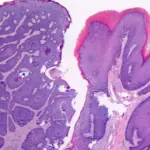
Basaloid anal transition zone tumor is the pattern mixed with squamous-basaloid. Basaloid tumors must be differentiated from a basal cell carcinoma extending from perianal skin.
What is the Pathology of Basaloid Anal Transition Zone Tumor?
The pathology of basaloid anal transition zone tumor is:
-Etiology: The cause of basaloid anal transition zone tumor is STD, increased spinchter tone, other diseases.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to basaloid anal transition zone tumor arises from the entodermal-ectodermal junctional zone of the anal canal at or above the dentate line particular the presence of palisading of the nuclei at the periphery of the clumps of tumour cells, but are potentially metastasizing tumours.
-Histology: The histology associated with basaloid anal transition zone tumor shows palisading solid circumscribed clumps of tumour cells containing small, round, or ovoid nuclei which are regular in shape and size.
How does Basaloid Anal Transition Zone Tumor Present?
Patients with basaloid anal transition zone tumor typically more in females at age of 41 to 80 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with basaloid anal transition zone tumor include the feeling of a lump or mass at the anal opening, persistent or recurring pain in the anal area, persistent or recurrent itching.
How is Basaloid Anal Transition Zone Tumor Diagnosed?
Basaloid anal transition zone tumor is diagnosed by anoscopy, flexible sigmoidoscopy, and biopsy.
How is Basaloid Anal Transition Zone Tumor Treated?
Basaloid anal transition zone tumor is treated by radiotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Basaloid Anal Transition Zone Tumor?
The prognosis of basaloid anal transition zone tumor is poor.