Blue nevus is a type of mole that is blue and can be congenital or acquired.
What is the Pathology of Blue Nevus?
The pathology of blue nevus is the study of the pathology and the histology of the proliferation of melanocytes.
-Etiology: The cause of blue nevus is not so clear but is believed to be caused by a lack of melanocytes to reach the dermis.
-Genes involved: BRAF and NRAS genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to blue nevus is believed that during development the melanocytes fail to reach the epidermis and get stuck below the epidermis.
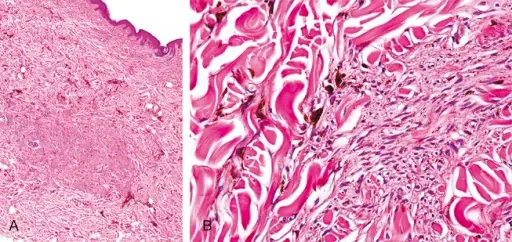
-Morphology: The morphology associated with blue nevus shows a uniform nucleus, large and round pale cytoplasm.
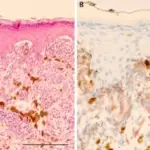
-Histology: The histology associated with blue nevus shows melanocytes that have a reduced amount of melanin, thickened collagen that is found in the dendritic spindles.
How does Blue Nevus Present?
Patients with blue nevus typically are common in women than in males and can occur at any stage of life but mostly in the second decade. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with blue nevus include small, round raised blue-colored and can be from 1-5 millimeters.
How is Blue Nevus Diagnosed?
This blue nevus is diagnosed by physical examination since it can be seen on the skin due to its blue appearance. Dermatoscopy is done in case one wants more information.
How is Blue Nevus Treated?
The blue nevus may be surgically removed.
What is the Prognosis of Blue Nevus?
The prognosis of blue nevus is good because the rarely becomes cancerous.