Bowenoid papulosis of the penis is a lesion established as papules, established as papules with and establish distinctive histopathology
What is the Pathology of Bowenoid Papulosis of the Penis?
The pathology of Bowenoid papulosis of the penis is:
-Etiology: The cause of Bowenoid papulosis of the penis is human papillomavirus (HPV) type 16.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Bowenoid papulosis of the penis usually appear as a papule or multiple papules after asymptomatic pivotal epidermal dysplasia and hyperplasia persuaded by HPV contagion.
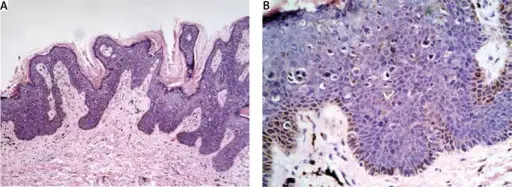
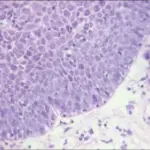
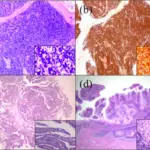
-Morphology: The morphology associated with Bowenoid papulosis of the penis shows penile intraepithelial neoplasia.
-Histology: The histology associated with Bowenoid papulosis of the penis shows full-thickness epidermal atypia, dyskeratotic cells, and atypical mitoses.
How does Bowenoid Papulosis of the Penis Present?
Patients with Bowenoid papulosis of the penis typically affect both genders equally, present at an age range of 31 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Bowenoid papulosis of the penis include inflamed pruritic lesions.
How is Bowenoid Papulosis of the Penis Diagnosed?
Bowenoid papulosis of the penis is diagnosed through biopsy. HPV subtyping may be needed.
How is Bowenoid Papulosis of the Penis Treated?
Bowenoid papulosis of the penis is treated through destructive or ablative therapies, 5 fluorouracil (5FU), carbon dioxide laser vaporization, electrocoagulation, cryotherapy, 5-aminolevulinic acid-mediated photodynamic therapy (ALA-PDT), and excisional surgery.
What is the Prognosis of Bowenoid Papulosis?
The prognosis of bowenoid papulosis is fair.