Bullous pemphigoid is an autoimmune disorder of the skin and mucosa that is chronic that occurs when the body attacks its cells.
What is the Pathology of Bullous Pemphigoid?
The pathology of bullous pemphigoid is:
-Etiology: The cause of bullous pemphigoid is immune mediated.
-Genes involved: None.
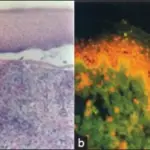
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to bullous pemphigoid is the deposition of antibodies IgG and complement in the basement membrane of the skin.
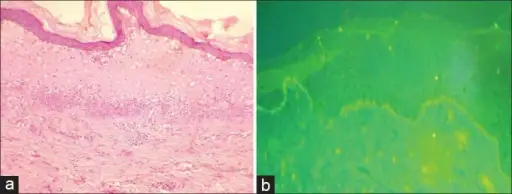
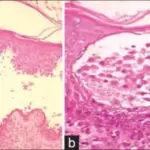
-Morphology: The morphology associated with bullous pemphigoid shows tense bullae filled with clear fulfilled in the sacs on the skin.
-Histology: The histology associated with bullous pemphigoid shows the presence of perivascular infiltrate of lymphocytes and some eosinophils, occasional neutrophils, superficial dermal edema.
How does Bullous Pemphigus Present?
Patients with bullous pemphigus typically is equal to both men and women. The elderly with a mean age of 65years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with bullous pemphigoid include the formation of bullae (generalized bullous form), small tense blisters (vesicular form), vegetative form, exfoliative erythroderma, and nodular.
How is Bullous Pemphigoid Diagnosed?
The bullous pemphigoid is diagnosed, histopathology, direct and indirect immunofluorescence.
How is Bullous Pemphigoid Treated?
The bullous pemphigoid is treated by use of anti-inflammatories, immunosuppressants.
What is the Prognosis of Bullous Pemphigoid?
The prognosis of bullous pemphigoid is fair since any fatality that occurs mostly occurs as a result of the medication.