Canalicular adenoma is a benign neoplasm of salivary glands.
What is the Pathology of Canalicular Adenoma?
The pathology of canalicular adenoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of canalicular adenoma may be related to alcohol use or smoking.
-Genes involved: CD117, BCL2, p63.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to canalicular adenoma is unknown.
-Morphology: Well-circumscribed small nodule.
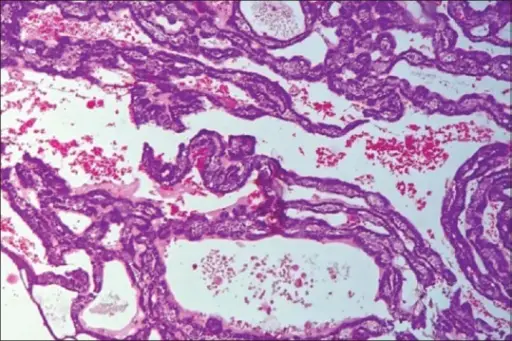
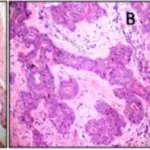
-Histology: Bilayered basaloid epithelial cells that make interconnected cords. There are also rows and tubular structures. Cystic dilation of canalicular structures may also be present edematous paucicellular stroma.
How does Canalicular Adenoma Present?
Patients with canalicular adenoma typically are females present at age range of from the 4th to 9th decades of life. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with canalicular adenoma include a painless mass that may be swollen.
How is Canalicular Adenoma Diagnosed?
Canalicular adenoma is diagnosed by physical exam and biopsy.
How is Canalicular Adenoma Treated?
Canalicular adenoma is treated by complete surgical excision.
What is the Prognosis of Canalicular Adenoma?
The prognosis of canalicular adenoma is good if properly treated.