Cardiac Hypertrophy or Ventricular Hypertrophy is a result of a compensatory heart muscle thickening when the heart is under increased stress.
What is the Pathology of Cardiac Hypertrophy?
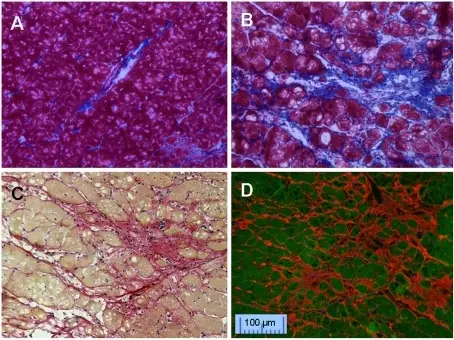
Cardiac hypertrophy pathology is characterized by a thickened heart muscle which results in smaller chambers and reduced pumping capacity of the heart.
How does Cardiac Hypertrophy Present?
Cardiac hypertrophy presents as shortness of breath with exertion, chest pain, arrhythmia, dizziness or syncope, chronic fatigue and leg edema.
How is Cardiac Hypertrophy Diagnosed?
Cardiac hypertrophy diagnosis is based on electrocardiogram, 2D echo, and MRI.
How is Cardiac Hypertrophy Treated?
Treatment for cardiac hypertrophy relies on early detection of the disease; medications such as beta blockers and calcium channel blockers relieve pressure on the heart, thereby preventing further thickening; surgery is also considered in advanced cases.
What is the Prognosis of Cardiac Hypertrophy?
Cardiac hypertrophy prognosis is good, with only 1% annual mortality.