Cataract is the clouding of the clear lens of the eye.
Examples of cataract include:
- Lenticular opacity
- Age-related cataract (nuclear sclerosis)
- Posterior subcapsular cataract
- Morganium cataract
What is the Pathology of Cataract?
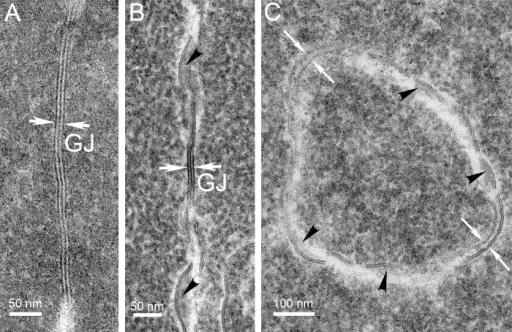
The pathology of cataract is diffusion of toxin with the ocular fluid supplied to the crystalline lens leading to development of opacification.
How does Cataract Present?
Cataract presents with blurred vision, and vision loss.
How is Cataract Diagnosed?
Cataract is diagnosed by comprehensive dilated eye examination, brightness acuity test, corneal topography, endothelial cell count.
How is Cataract Treated?
Cataract is treated with a balanced diet, UV blocking sunglasses, phacoemulsification, and extracapsular cataract extraction if indicated.
What is the Prognosis of Cataract?
The prognosis of cataract is an excellent prognosis in the case of a cataract extraction, although primary pathology plays an important role in the final visual prognosis.