Cell signaling is the fundamental process by which specific information is transferred from the cell surface to the cytosol and ultimately to the nucleus.
What is Cell Signaling?
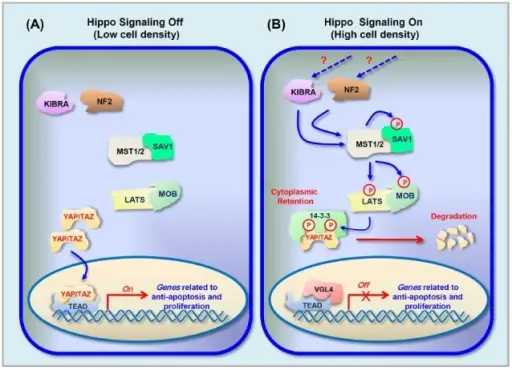
Cell Signaling. Hippo signaling pathway. Schematic diagram for the core components and signal transduction of Hippo pathway. (A) When Hippo signaling is Off (in low cell density): The kinases MST1/2 and LATS are inactive, which results in inhibition of phosphorylation of YAP and TAZ. The stabilized YAP/TAZ in nuclei interacts with TEAD and enhances the transcription of target genes related to anti-apoptosis and proliferation. (B) When Hippo signaling is On (in high cell density): Activation of KIBRA and NF2 via unknown upstream signaling leads to activation of MST1/2. Activated MST1/2 phosphorylate SAV1 which in turn phosphorylate LATS and MOB1. The activated LATS/MOB phosphorylates YAP/TAZ which results in cytoplasmic retention by 14-3-3 protein and proteasomal degradation of YAP/TAZ. As a result, TEAD interacts with VGL4 and suppresses the expression of target genes. Cross-talk between Wnt/β-catenin and Hippo signaling pathways: a brief review. Kim M, Jho EH - BMB reports (2014). Not Altered. CC.