Central pontine myelinolysis is a neurological disorder that most frequently occurs after too rapid medical correction of sodium deficiency. The rapid rise in sodium concentration is accompanied by the movement of small molecules and pulls water from brain cells. The shift in water and brain molecules leads to the destruction of myelin. Certain areas of the brain are particularly susceptible to myelinolysis, especially the pons.
What is Central Pontine Myelinolysis?
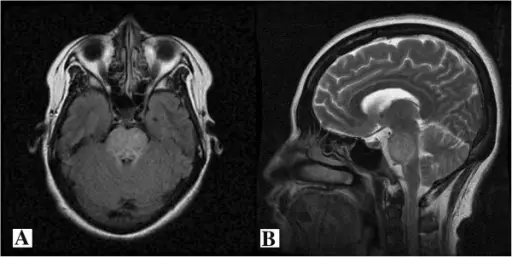
MRI of the brain revealed symmetric, high-intensity signal in the pons with sparing of the peripheral portion, suggesting central pontine myelinolysis (A, axial view and B, sagittal view).Plasma exchange successfully treats central pontine myelinolysis after acute hypernatremia from intravenous sodium bicarbonate therapy.
Chang KY, Lee IH, Kim GJ, Cho K, Park HS, Kim HW - BMC nephrology (2014). Not Altered. CC.