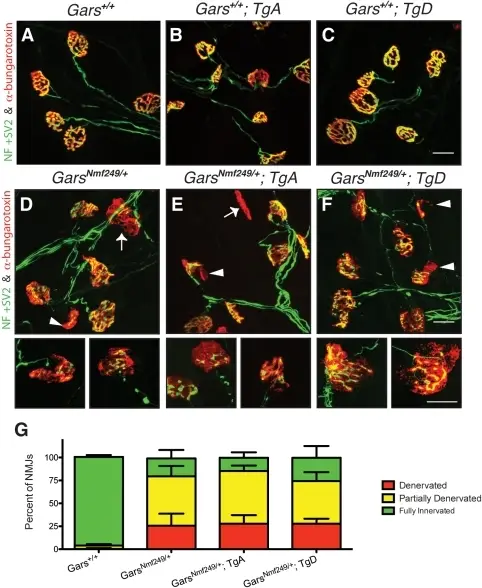
Charcot-Marie-tooth disease is an inherited neurological disorder that affects both sensory and motor nerves.
What is the Pathology of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease?
The pathology of Charcot-Marie-tooth disease is the study of the motor and the sensory disease of the nerves.
-Etiology: The cause of charcot-marie-tooth disease is gene mutation.
-Genes involved: GARS, PMP22, ATP1A1, PRPS1 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to charcot-marie-tooth disease is increased duplication of the genes involved in the myelin sheath leading to the abnormality of the affected areas.
-Morphology: NA.
-Histology: NA.
How does Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Present?
Patients with charcot-marie-tooth disease typically are women present at the age range of childhood to 20 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with charcot-marie-tooth include tripping and falling a lot, stork leg appearance due to muscle loss, bony abnormalities- high arch and hammertoes, sharp pain of the limbs, and emaciation.
How is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Diagnosed?
Charcot-marie-tooth disease is diagnosed by physical examination, history taking, neurology, and electrocardiography.
How is Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease Treated?
Charcot-marie-tooth disease is treated by correction of the deformities, tendon lengthening, occupation therapy, and also pain medication.
What is the Prognosis of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease?
The prognosis of charcot-marie-tooth disease is good since one with the disease can live a normal life with supportive therapy.