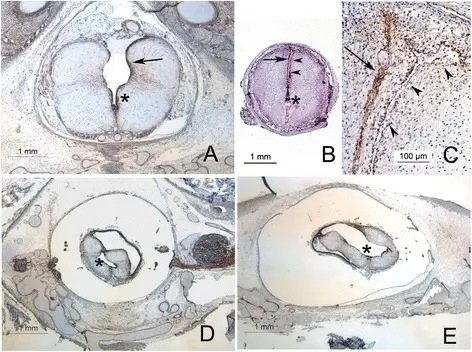
Chiari type II malformation is a relatively common congenital malformation of the spine and posterior fossa characterized by myelomeningocele and a small posterior fossa with the descent of the brainstem, vermis, and cerebellar tonsils.
What is the Pathology of Chiari Type II Malformation?
Etiology: The cause of Chiari type II malformation is unknown.
Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Chiari type II malformation is due to in utero malformation of the cranial structures and spine.
Histology: The histology associated with Chiari type II malformation shows dysplastic large fibrous tissue along with choroid plexus.
How does Chiari Type II Malformation Present?
Patients with Chiari type II malformation are more often females than males, and the condition is congenital. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Chiari type II malformation include hydrocephalus, loss of strength, abnormal breathing, and depressed gag reflex.
How is Chiari Type II Malformation Diagnosed?
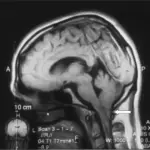
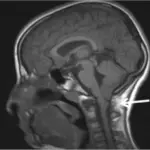
Chiari type II malformation is diagnosed via MRI and CT scan.
How is Chiari Type II Malformation Treated?
Chiari type II malformation is treated surgically.
What is the Prognosis of Chiari Type II Malformation?
The prognosis of Chiari type II malformation is poor.