Cholangiocarcinoma is a type of cancer that forms in the slender tubes (bile ducts) that carry the digestive fluid bile.
What is the Pathology of Cholangiocarcinoma?
The pathology of cholangiocarcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of cholangiocarcinoma is scarring of the liver or chronic liver disease.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
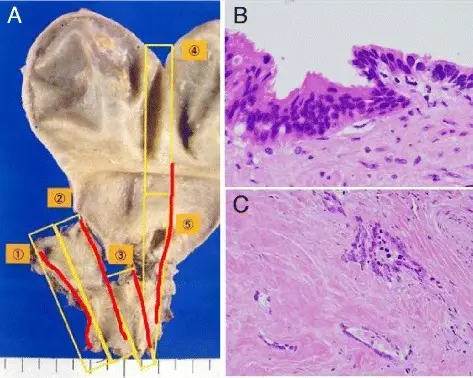
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cholangiocarcinoma arises from the malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the intrahepatic or extrahepatic bile ducts.
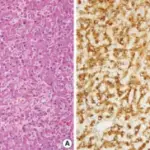
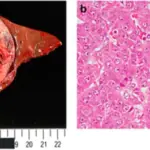
-Histology: The histology associated with cholangiocarcinoma shows desmoplastic stroma-rich adenocarcinoma with cholangiocyte differentiation.
How does Cholangiocarcinoma Present?
Patients with cholangiocarcinoma typically affect older males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cholangiocarcinoma include jaundice, intensely itchy skin, white-colored stools, fever, and weight loss.
How is Cholangiocarcinoma Diagnosed?
Cholangiocarcinoma is diagnosed through liver function tests, tumor markers, CT, MRI, ultrasound, and biopsy.
How is Cholangiocarcinoma Treated?
Cholangiocarcinoma is treated through surgical excision, liver transplant, targeted drug therapy, and chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Cholangiocarcinoma?
The prognosis of cholangiocarcinoma is fair.