Chronic abacterial prostatitis is the inflammation of the prostate due to recurrent attacks of acute bacterial prostatitis with no history of urinary tract infections.
What is the Pathology of Chronic Abacterial Prostatitis?
The pathology of chronic abacterial prostatitis is:
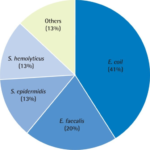
-Etiology: The cause of chronic abacterial prostatitis is pathogens such as chlamydia trachomatis and ureaplasma urealyticum
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to chronic abacterial prostatitis is unknown.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with chronic abacterial prostatitis shows enlarged, fibrosis, and shrunken prostate.
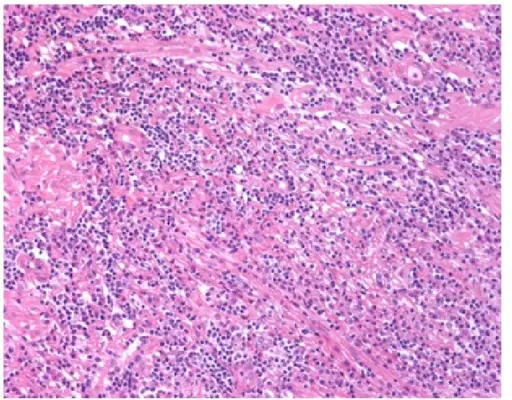
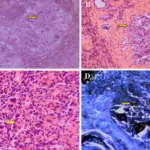
-Histology: The histology associated with chronic abacterial prostatitis shows foci of lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, and neutrophils within the prostatic substance.
How does Chronic ABacterial Prostatitis Present?
Patients with chronic abacterial prostatitis are typically older males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with chronic abacterial prostatitis include; hematuria, dysuria, malodorous urine, urinary urgency/ frequency, urinary retention, and urethral discharge.
How is Chronic Abacterial Prostatitis Diagnosed?
Chronic abacterial prostatitis is diagnosed through history and physical examination. Laboratory studies such as urinalysis may be useful to rule out oother conditions. .
How is Chronic Abacterial Prostatitis Treated?
Chronic abacterial prostatitis is treated through medical care- antimicrobial therapy, alpha-blockers, and pain medication. Surgical intervention- transurethral resection of the prostate and transurethral vaporization of the prostate.
What is the Prognosis of Chronic Abacterial Prostatitis?
The prognosis of chronic abacterial prostatitis is fair with treatment success rates of about 40%-75%. Common to relapses.