Chronic cholecystitis is the chronic inflammation of the gallbladder, typically secondary to gallstones and cholelithiasis.
What is the Pathology of Chronic Cholecystitis?
The pathology of chronic cholecystitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of chronic cholecystitis is cholelithiasis.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to chronic cholecystitis may be due to recurrent acute cholecystitis, or cholelithiasis.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with chronic cholecystitis shows gallbladder wall thickening.
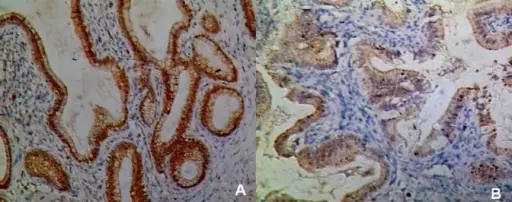
-Histology: The histology associated with chronic cholecystitis shows variable amounts of predominantly mononuclear inflammatory infiltrate in lamina propria.
How does Chronic Cholecystitis Present?
Patients with chronic cholecystitis typically are female present at the age range of from 18 to 50 years-old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with chronic cholecystitis include Murphy sign or the right upper abdominal pain with deep palpation, abdominal discomfort often related to fatty food ingestion, nausea, and vomiting.
How is Chronic Cholecystitis Diagnosed?
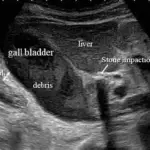
Chronic cholecystitis is diagnosed with abdominal ultrasound, abdominal CT with contrast, or HIDA (hepatobiliary iminodiacetic acid) scan demonstrating a reduced ejection fraction (< 35%).
How is Chronic Cholecystitis Treated?
Chronic cholecystitis is treated with elective cholecystectomy.
What is the Prognosis of Chronic Cholecystitis?
The prognosis of chronic cholecystitis is good.