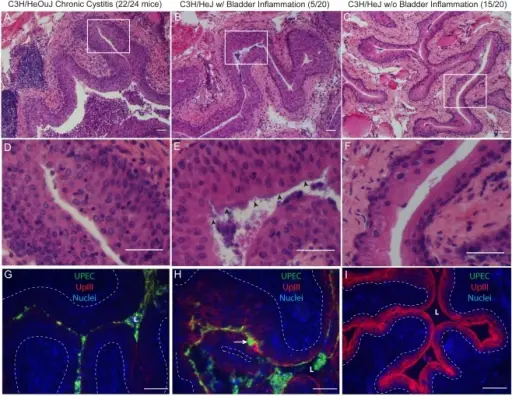
Chronic Cystitis. Chronic bladder infection in C3H/HeJ mice is histologically distinct from chronic cystitis in C3H/HeOuJ mice.Representative paraffin-embedded, fixed bladder sections from C3H/HeOuJ mice with chronic cystitis (22 out of 24 mice; panels A, D, & G), C3H/HeJ mice with high bacterial burdens and evidence of bladder inflammation (5 out of 20 mice; panels B, E, & H), and the remaining C3H/HeJ mice that uniformly lacked evidence of bladder inflammation (15 out of 20 mice; panels C, F, & I) were analyzed at 4 wpi; Bars approximate 50 µm in length. A–F, Sections were stained with hematoxylin & eosin and examined by light microscopy; boxes in panels A–C demarcate boundaries of higher magnification images in panels D–F. G–I, Sections were analyzed by indirect immunofluorescence (IF) microscopy, staining for E. coli (green) and uroplakin III (red), with nuclei counterstained with bis-benzimide (blue). “L” denotes bladder lumen; dashed line indicates approximate location of basement membrane; arrowheads point to urothelial surface bacterial colonization in panel E; and the white arrow points to a mature superficial facet cell containing a possible IBC in panel H. Early severe inflammatory responses to uropathogenic E. coli predispose to chronic and recurrent urinary tract infection. Hannan TJ, Mysorekar IU, Hung CS, Isaacson-Schmid ML, Hultgren SJ - PLoS pathogens (2010). Not Altered. CC.
Chronic cystitis is a chronic inflammatory condition of the bladder that is refractory to treatment or surgical correction.
What is the Pathology of Chronic Cystitis?
The pathology of chronic cystitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of chronic cystitis is bacterial pathogens.
-Genes involved: HSPA1B, CXCR1 & 2, TLR2, TLR4, TGF-β1 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to chronic cystitis is obstruction and stasis of urine flow.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with chronic cystitis shows red, friable, heaped and ulcerated mucosa on cystoscopy.
-Histology: The histology associated with chronic cystitis shows small vessels radiating towards a central scar.
How does Chronic Cystitis Present?
Patients with chronic cystitis typically affect women more commonly than males in 30 to 50 years of age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with chronic cystitis include variable symptoms, including discomfort with bladder filling and relief with voiding.
How is Chronic Cystitis Diagnosed?
The diagnosis of chronic cystitis is usually made clinically, with urine culture, and urinalysis.
How is Chronic Cystitis Treated?
Chronic cystitis is treated with corrective surgical treatment of anatomic pathology, immunomodulatory therapy, and antibiotics.
What is the Prognosis of Chronic Cystitis?
The prognosis of chronic cystitis is good with appropriate treatment.