Chronic glomerulonephritis is a disease of the kidney in which the inflammation caused leads to scarring, slow and cumulative damage of the kidney.
What is the Pathology of Chronic Glomerulonephritis?
The pathology of chronic glomerulonephritis is:
-Etiology: The cause of chronic glomerulonephritis is infections bacterial or viral, autoimmune diseases,
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to chronic glomerulonephritis glomerular scarring, leading to cortical tubular atrophy, interstitial fibrosis and infiltration.
-Morphology: Not applicable.
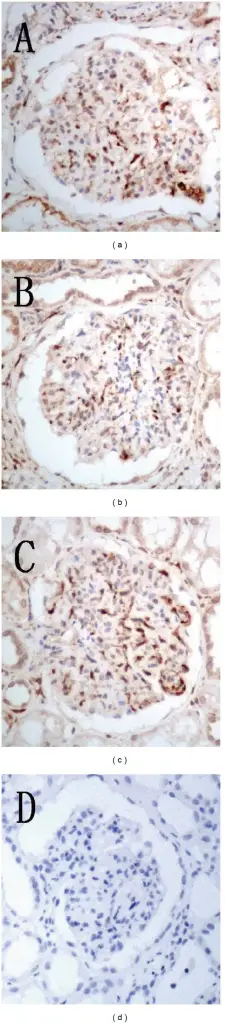
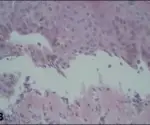
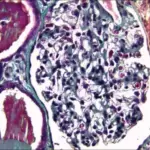
-Histology: The histology of chronic glomerulonephritis shows partial and complete hyalinization of glomeruli. There may also be an inflammatory infiltrate.
How does Chronic Glomerulonephritis Present?
Patients with chronic glomerulonephritis typically bothe male and female but men reach kidney failure faster than male present at age range of 18-65 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with chronic glomerulonephritis include blood in urine, confusion, drowsiness, lethargy, foamy urine, loss of sensation in the lower limbs.
How is Chronic Glomerulonephritis Diagnosed?
Chronic glomerulonephritis is diagnosed with complete blood count, kidney biopsy and scan, history taking, physical examination and, urinalysis.
How is Chronic Glomerulonephritis Treated?
Chronic glomerulonephritis is treated by managing the symptoms. Antihypertensives, diuretics, corticosteroids, dietary restrictions, immunosuppressives, dialysis, a kidney transplant.
What is the Prognosis of Chronic Glomerulonephritis?
The prognosis of chronic glomerulonephritis is: