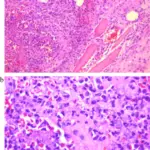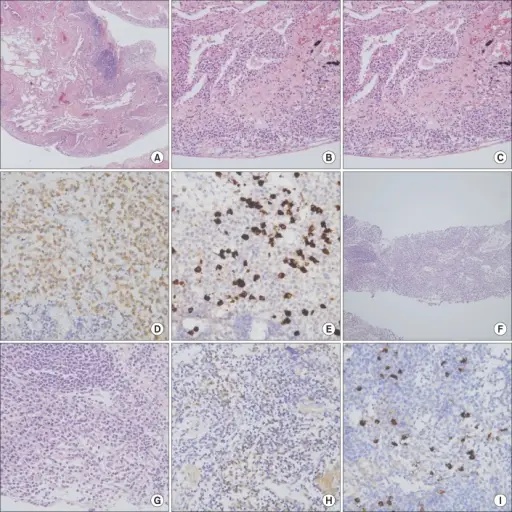
(A-E) Pleural biopsy showed chronic inflammation with lymphoplasmacytic infiltration and fibrosis (A, H&E stain, ×40; B, H&E stain, ×200; C, H&E stain, ×400; D, immunohistochemical stain for IgG, ×400; E, immunohistochemical stain for IgG4, ×400). (F-I) Lymph node biopsy of the neck on the previous admission also showed chronic inflammation with lymphoplasmacytic infiltration. A Case of IgG4-Related Disease Presenting as Massive Pleural Effusion and Thrombophlebitis: Choi JH, Sim JK, Oh JY, Lee EJ, Hur GY, Lee SH, Lee SY, Kim JH, Lee SY, Shin C, Shim JJ, In KH, Kang KH, Min KH - Tuberculosis and respiratory diseases (2014). Not altered. CC.
Chronic inflammation is the long term response to an injury or infection.
Summary of Chronic Inflammation: Infiltration of lymphocytes, and deposition of scar tissue.
Causes of Chronic Inflammation Include:
- Long term acute inflammation
- Long term exposure to irritants
- Autoimmune conditions
Mediators of Chronic Inflammation Include:
- Vasoactive amines (histamine and serotonin)
- Peptides (bradykinin)
- Eicosanoids (prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotriens)
Morphologic Features of Chronic Inflammation Include:
- Lymphocytes
- Macrophages
- Fibrous tissue
- Interspersed fibroblasts
- Granulomas