Chronic ischemic heart disease is a condition of recurring chest pain due to inadequate blood supply to the heart caused by narrowed heart arteries.
What is the Pathology of Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease?
Chronic ischemic heart disease pathology is caused by narrowing of heart arteries.
How does Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease Present?
Chronic ischemic heart disease presents as extreme chest pain and/or shortness of breath. Chronic ischemic heart disease is relieved by medication or rest, radiates to the back, arm or other areas occurring repeatedly. Symptoms usually occur during periods of physical exertion and last <5 minutes.
How is Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease Diagnosed?
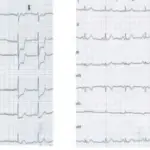
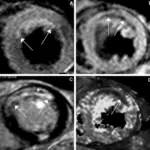
Chronic ischemic heart disease is diagnosed with thorough history and physical exam, routine blood test, electrocardiogram and stress test.
How is Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease Treated?
Chronic ischemic heart disease is treated with ACE inhibitors, ARBs, antiplatelet drugs, beta blockers, calcium channel blockers, nitrates, and statins. Surgical procedures can also be performed such as angioplasty, and coronary artery bypass graft.
What is the Prognosis of Chronic Ischemic Heart Disease?
Chronic ischemic heart disease prognosis is dependent on disease progression. Good prognosis is achieved in patients with good control of risk factors and those who received appropriate treatment.