Chronic liver failure is the loss of liver function due to cirrhosis.
What is the Pathology of Chronic Liver Failure?
The pathology of chronic liver failure is:
-Etiology: The cause of chronic liver failure is cirrhosis hepatitis A, hepatitis B, alcoholic liver disease, and Primary biliary cholangitis.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to chronic liver failure includes inflammation (chronic hepatitis), liver cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
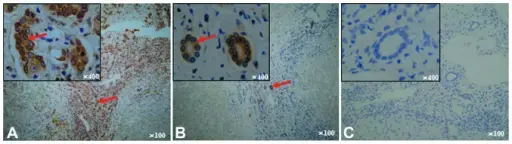
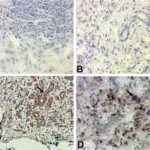
-Histology: The histology associated with chronic liver failure shows regenerative nodules of hepatocytes surrounded by fibrous bands without central veins.
How does Chronic Liver Failure Present?
Patients with chronic liver failure typically affect males present at the age range of 35-55 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with chronic liver failure include gynecomastia, testicular atrophy, and anaemia.
How is Chronic Liver Failure Diagnosed?
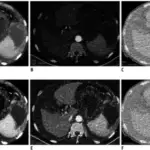
Chronic liver failure is diagnosed using blood tests, ultrasound, and biopsy of the liver.
How is Chronic Liver Failure Treated?
Chronic liver failure is treated with corticosteroids, interferon, antivirals, bile acids, or liver transplant.
What is the Prognosis of Chronic Liver Failure?
The prognosis of chronic liver failure with compensation is good with a survival rate of 15 years.