Cocaine injury is the injury caused by the overuse of cocaine.
What is the Pathology of Cocaine Injury?
The pathology of cocaine injury is:
-Etiology: The cause of cocaine injury is thrombus formation
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cocaine injury associated with cardiac is coronary artery vasoconstriction and accelerated atherosclerosis, and by initiating thrombus formation.
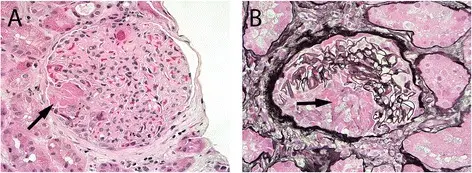
-Morphology: The morphology associated with cocaine injury shows coronary artery vasoconstriction.
-Histology: The histology associated with cocaine injury shows hyperplastic endoplasmic reticulum with necrosis.
How does Cocaine Injury Present?
Patients with cocaine injury typically affect males and females both present at the age range of 20-55. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cocaine injury include loss of sense of smell, nosebleeds, problems with swallowing, hoarseness, and an overall irritation of the nasal septum leading to a chronically inflamed, runny nose.
How is Cocaine Injury Diagnosed?
Cocaine injury is diagnosed with a blood test.
How is Cocaine Injury Treated?
Cocaine injury is treated with nitroglycerin if the injury is associated with chest pain, beta receptor antagonist, antiarrhythmics.
What is the Prognosis of Cocaine Injury?
The prognosis of cocaine injury is fair if treated promptly.