Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is an immune system disorder that causes to have low levels of the proteins that help fight infections. Patients with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) are likely to have repeated infections in ears, sinuses and respiratory system.
What is the Pathology of Common Variable Immunodeficiency?
The pathology of common variable immunodeficiency is:
-Etiology: The cause of common variable immunodeficiency is mutations in the genes which result in dysfunctional B cells that cannot make sufficient amounts of antibodies. about 10 percent of cases, CVID is hereditary.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to common variable immunodeficiency defective B cell function leading to impaired immunoglobulin production causing recurrent infections, chronic lung disease, autoimmune disorders, gastrointestinal disease, or increased risk of malignancy.
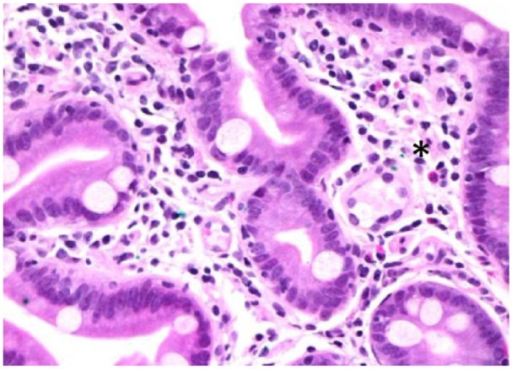
-Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with common variable immunodeficiency are immune dysregulations, malignancy, and recurrent infections.
How does Common Variable Immunodeficiency Present?
Patients with common variable immunodeficiency reported as earlier onset of symptoms and diagnosis in males however, common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) does not show any predilection for race or gender. Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is most frequently diagnosed in adults aged 20 to 40 years old. In some cases common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) may become obvious during childhood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with common variable immunodeficiency include: breathing issues, chronic cough, diarrhea, weight loss, frequent ear infections, and recurrent sinus infections.
How is Common variable immunodeficiency Diagnosed?
Common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) diagnosis can be made through screening tests that measure immunoglobulin levels or the number of B cells in the blood. immunofluorescence staining is mostly involved for laboratory tests of serum IgA, IgG and IgM levels which are decreased or absent in the disease.
How is Common Variable Immunodeficiency Treated?
Common variable immunodeficiency is treated by intravenous immunoglobulin infusions or subcutaneous (under the skin) immunoglobulin injection to partially restore immunoglobulin levels. The mainstay of treatment for common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) is Ig replacement therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Common Variable Immunodeficiency?
The prognosis of common variable immunodeficiency is reasonably good unless severe autoimmune disease or malignancy develops. There is no cure for common variable immunodeficiency (CVID). With ongoing treatment, many people with common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) live active and fulfilling lives. In some cases, complications of common variable immunodeficiency (CVID) such as lung damage or cancer may affect life expectancy. These complications appear over time. They may become life-threatening, but that process often takes years.