Condyloma acuminatum is known as anogenital warts, manifestations of HPV infection that occur in a subset of individuals with anogenital HPV infection.
What is the Pathology of Condyloma Acuminatum?
The pathology of condyloma acuminatum is:
-Etiology: The cause of condyloma acuminatum is human papillomavirus HPV.
-Genes involved: TLR2 597.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to condyloma acuminatum are cells of the basal layer of the epidermis are invaded by human papillomavirus HPV. These penetrate through skin and cause mucosal microabrasions.
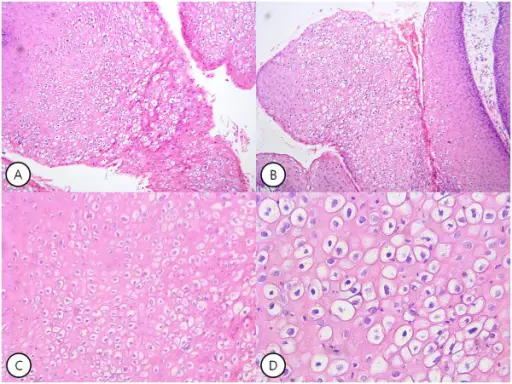
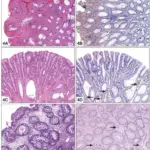
-Histology: The histology associated with condyloma acuminatum generally demonstrates disruption of the epidermis with hyperkeratosis, coarse keratohyaline granules, and koilocytes in a prominent granular layer. The epidermis or mucosa of flat condylomata demonstrates acanthosis.
How does Condyloma Acuminatum Present?
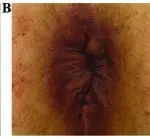
Patients with condyloma acuminatum typically are all genders at age range of 18–59 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with condyloma acuminatum include: small, skin-colored or gray spots in your genital area that are raised or flat, several warts close together that are shaped like a cauliflower, itching or discomfort in your genital area.
How is Condyloma Acuminatum Diagnosed?
Condyloma acuminatum is diagnosed clinically.
How is Condyloma Acuminatum Treated?
Condyloma acuminatum is treated by: cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid, surgical excision, electrosurgery, and laser therapy.
What is the Prognosis of Condyloma Acuminatum?
The prognosis of condyloma acuminatum is good. It is cleared up without any intervention within a few months after acquisition, and about 90% clear within 2 years. The treatment can be delayed in children, adolescents, and young, healthy adults, as lesions often resolve spontaneously over months to years.