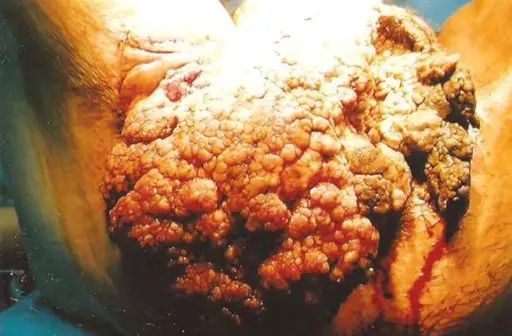
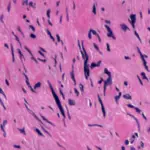
Condyloma acuminatum is a benign tumor caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) types 6 and 11.
What is the Pathology of Condyloma Acuminatum?
The pathology of condyloma acuminatum is:
-Etiology: The cause of condyloma acuminatum is human papillomavirus types 6 and 11.
-Genes involved: p63.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to condyloma acuminatum invading of the basal epidermal cells layer by HPV. These cause mucosal microabrasions. No signs and symptoms at the latent viral phase. The making of viral DNA, particles, and capsids begin. Epidermal cells infected and mature the morphologic uncharacteristic koilocytosis of condyloma acuminatum.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with condyloma acuminatum shows single or numerous stalkless or pedunculated, red papillary carbuncles varying from 1 mm to several millimeters in diameter.
-Histology: The histology associated with condyloma acuminatum shows papillary villi with connective tissue stroma enclosed by squamous epithelium that displays hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis, and hyperplasia of the prickle cell layer.
How does Condyloma Acuminatum Present?
Patients with condyloma acuminatum typically affect both genders present at an age range of 20-24 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with condyloma acuminatum include pruritus, painless bumps, discharge, or multiple lesions.
How is Condyloma Acuminatum Diagnosed?
Condyloma acuminatum is diagnosed through laboratory studies, physical exam, and biopsy. Pap smears may check for papillomatosis, and acetowhitening will show a shiny white snowy appearance.
How is Condyloma Acuminatum Treated?
Condyloma acuminatum is treated through treatment routines and follow-up care. Cryotherapy, Curettage, Surgical excision. Carbon dioxide laser action for widespread and recurring condyloma acuminatum.
What is the Prognosis of Condyloma Acuminatum?
The prognosis of condyloma acuminatum is poor as it either fail to respond to management or reappears after a response.