Cystic fibrosis is an inherited disorder of chloride ion transport that affects fluid secretion in exocrine glands and in epithelial lining of respiratory, gestational, and reproductive tracts. Cystic fibrosis is commonly due to Delta-F508 genetic mutation.
What is the Pathology of Cystic Fibrosis?
The pathology of (cystic fibrosis) is:
–Etiology: The cause of cystic fibrosis is a change, or mutation, in a gene called CFTR (cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator). This gene controls the flow of salt and fluids in and out of your cells.
–Genes involved: CFTR, delta-F508
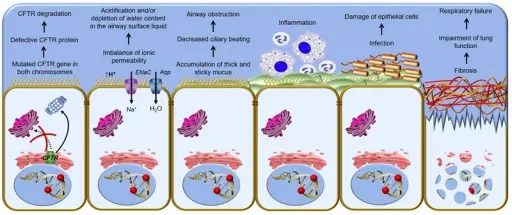
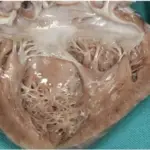
–Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cystic fibrosis are due to defective CFTR proteins that results in defective cellular ion transport. This causes buildup of thick mucus throughout certain organs of the the body, leading to respiratory insufficiency, along with many other systemic obstructions and abnormalities.
–Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with cystic fibrosis are hyperplasia of mucous cells, increased numbers of pulmonary neuroendocrine and indeterminate cells, and degeneration and sloughing of epithelial cells.
How does Cystic Fibrosis Present?
Patients with cystic fibrosis are typically males but females can get it too. It is present mostly from childhood to above 50 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cystic fibrosis include a persistent cough, wheezing, and salty skin.
How is Cystic Fibrosis Diagnosed?
Cystic fibrosis is diagnosed by a sweat chloride test, which measures the amount of chloride in sweat. Cystic fibrosis may also be diagnosed with genetic tests for the delta F508 mutation. Chest X rays may be helpful to assess pulmonary structure.
How is Cystic Fibrosis Treated?
Cystic fibrosis is treated by symptomatic management treatments only including Trikafta, antibiotics to prevent and treat chest infections, medicines to make the mucus in the lungs thinner and easier to cough up.
What is the Prognosis of Cystic Fibrosis?
The prognosis of cystic fibrosis is fair. There is no cure for cystic fibrosis. Lung disease eventually worsens to the point where the person is disabled. The average life span for people with cystic fibrosis who live to adulthood is about 44 years old. Death is most often caused by lung complications.