Cystitis cystica is a rare chronic reactive inflammatory disorder thought to be caused by chronic irritation of the urothelium because of infection, calculi, outlet obstruction, or tumor resulting in multiple small filling defects in the bladder wall.
What is the Pathology of Cystitis Cystica?
The pathology of cystitis cystica is:
-Etiology: The cause of cystitis cystica is chronic irritation and local inflammatory insult.
-Genes involved: No associated genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cystitis cystica is a reactive process in response to chronic irritation, infection, calculi, outlet obstruction, catheterization. Urothelium proliferates and invaginates into underlying lamina propria.
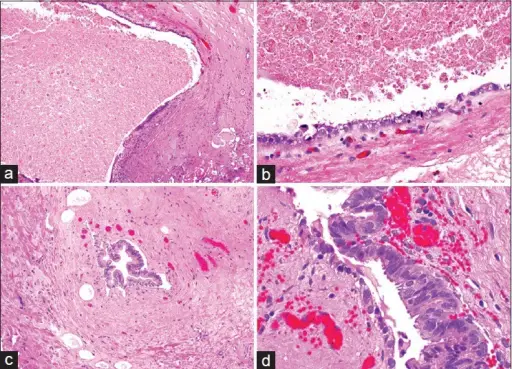
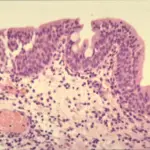
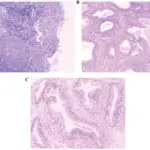
-Morphology: The morphology associated with cystitis cystica shows translucent submucosal cysts, mostly < 5 mm diameter.
-Histology: The histology associated with cystitis cystica shows abundant urothelial von Brunn nests. Often exhibit a vaguely lobular distribution of invaginations.
How does Cystitis Cystica Present?
Patients with cystitis cystica typically affect both males and females at any age. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cystitis cystica include the following. The majority are asymptomatic incidental findings.
How is Cystitis Cystica Diagnosed?
Cystitis cystica is diagnosed by microscopic examination of resected tissue.
How is Cystitis Cystica Treated?
Cystitis cystica is treated by the elimination of underlying sources of irritation. Antibiotic therapy is associated with chronic urinary tract infections. Occasionally surgical resection (transurethral) may be necessary.
What is the Prognosis of Cystitis Cystica?
The prognosis of cystitis cystica is variable. It is a reactive process without malignant potential. May regress if the cause of irritation is removed.