Cytomegalovirus is a kind of herpesvirus which usually produces very mild symptoms but may cause severe neurological damage in people with weakened immune systems and in the newborn.
What is the Pathology of Cytomegalovirus?
The pathology of cytomegalovirus is:
-Etiology: The cause of cytomegalovirus is direct contact with saliva or urine, sexual contact, bone marrow transplantation.
-Genes involved: UL35, UL73, UL74, UL75, UL100, and UL115.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to cytomegalovirus are: Upon initial infection, CMV infects the epithelial cells of the salivary gland, resulting in a persistent infection and viral shedding.
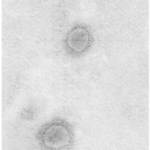
-Morphology: The morphology associated with cytomegalovirus shows outer lipid bilayer envelope, composed of various viral glycoproteins, followed by the tegument, a proteinaceous matrix, which holds double stranded linear DNA core in an icosahedral nucleocapsid. The virion is usually spherical in composition.
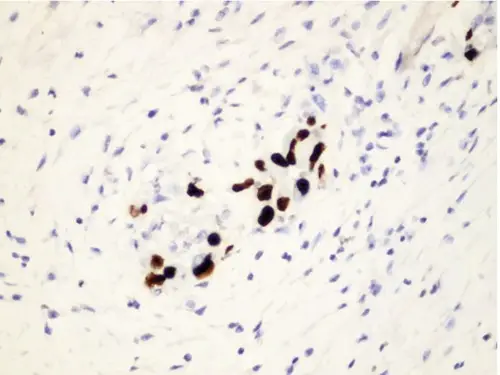
-Histology: The histology associated with cytomegalovirus shows thickened nuclear membrane, coarse red intracytoplasmic granules and increased apoptotic bodies.
How does Cytomegalovirus Present?
Patients with cytomegalovirus typically are all genders at all ages. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with cytomegalovirus include feeling sick, sore throat, swollen glands, tiredness, skin rash, a high temperature, and aching muscles.
How is Cytomegalovirus Diagnosed?
Cytomegalovirus is diagnosed by laboratory tests such as PCR.
How is Cytomegalovirus Treated?
Cytomegalovirus is treated by antiviral medications.
What is the Prognosis of Cytomegalovirus?
The prognosis of cytomegalovirus is good. Most patients recover completely.