Dermatomyositis is a type of inflammatory myopathy with distinct cutaneous manifestations.
What is the Pathology of Dermatomyositis?
The pathology of dermatomyositis is:
-Etiology: The cause of dermatomyositis is associated with genetic, immunologic, infectious, and environmental causes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to dermatomyositis starts with an exogenous factor triggering the inflammatory cascade, with antibodies directed against endothelial cells resulting to the membrane attack complex’d deposition on capillaries resulting to endothelial damage, capillary necrosis, ischemia, and myofibril necrosis.
-Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with dermatomyositis skin findings are heliotrope rash, dilated capillary loops, Gottron papules, V sign, Shawl sign, and Mechanic’s hands.
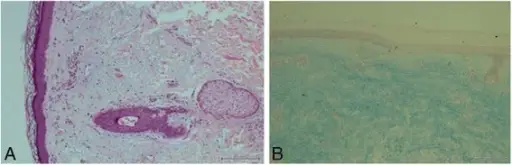
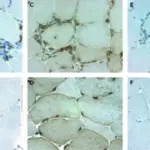
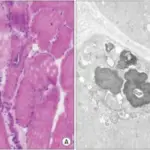
– Histologic changes: The histologic findings associated with dermatomyositis is the perifascicular atrophy with/without perimysial and perivascualr inflammatory infiltrates, as well as tuboreticular inclusion in the intramuscular arterioles and capillaries.
How does Dermatomyositis Present?
Patients with dermatomyositis are typically women. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with dermatomyositis include an initial manifestation of skin disease, that is preceded or followed by muscle disease that present as weakness and tenderness. Extramuscular manifestation include fever, arthralgia, malaise, weight loss, Raynaud phenomenon, dysphagia, gastroesophageal reflux, atrial-ventricular defects, tachyarrythmias, dilated cardiomyopathies, gastro-intestinal ulcers and infections, joint contractures, and pulmonary issues.
How is Dermatomyositis Diagnosed?
Dermatomyositis is diagnosed through laboratory testing (muscle enzyme levels) and diagnostic exams (magnetic resonance imaging, chest radiography, ultrasonography, electromyography, or computed tomography).
How is Dermatomyositis Treated?
Dermatomyositis is treated using general and specific treatments. Bed rest is advised for patients with severe muscle inflammation and rehabilitation for those with joint contractures. For muscle disease, first line treatments include corticosteroids and steroid sparing immunosuppressive drugs.
What is the Prognosis of Dermatomyositis?
The prognosis of dermatomyositis is good with most of the patients experience spontaneous remission and only 5% leading to disease progression and death.