Diastolic dysfunction is a heart condition that causes left heart failure, where the heart chamber does not appropriately expand, causing inadequate filling of the chambers and blood backing up to the organs.
What is the Pathology of Diastolic Dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction is characterized by stiffening of the heart muscles, thereby limiting its stretch, leading to inadequate filling of blood.
How does Diastolic Dysfunction Present?
Diastolic dysfunction affects more than 25% of adults more than 40 years old. It presents as a progressive shortness of breath on exertion, easy fatigability, and water retention in lower extremities.
How is Diastolic Dysfunction Diagnosed?
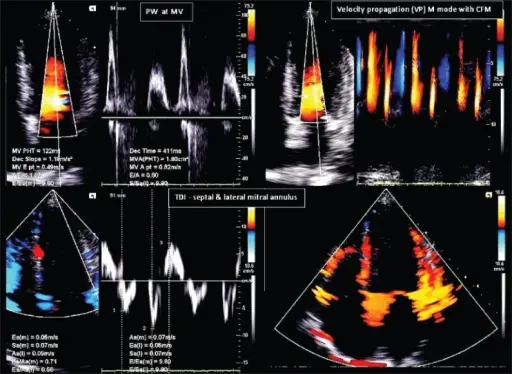
Diastolic dysfunction can be diagnosed with the use of 2D echo.
How is Diastolic Dysfunction Treated?
Diastolic dysfunction is treated symptomatically with ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, ARBs, and beta blockers. Prevention includes smoking cessation, lifestyle modification, and adequate control of hypertension.
What is the Prognosis of Diastolic Dysfunction?
Diastolic dysfunction prognosis is moderate with annual mortality of 5-8%.