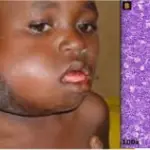
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is a neoplasm of large B lymphoid cells with nuclei at least twice the size of a lymphocyte.
What is the Pathology of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma?
The pathology of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is due to dysregulation of BCL6, overexpression of BCL2 and mutations in p300 and CREBP.
-Genes involved: BCL6, BCL2, p300 and CREBP genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma include dysregulation of BCL6, overexpression of BCL2 and mutations in p300 and CREBP.
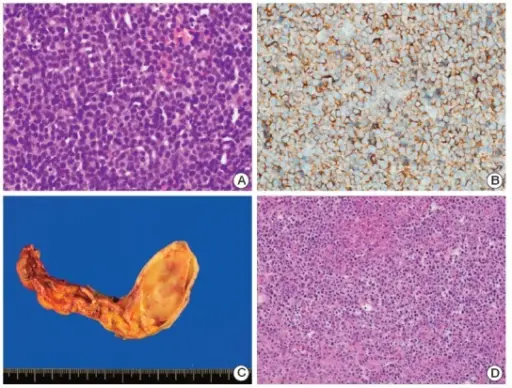
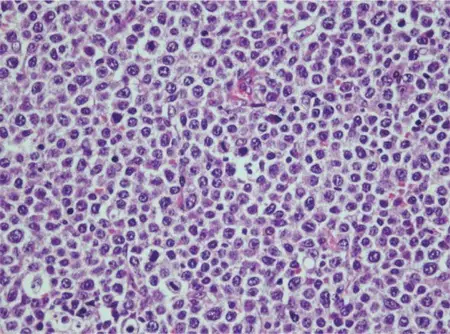
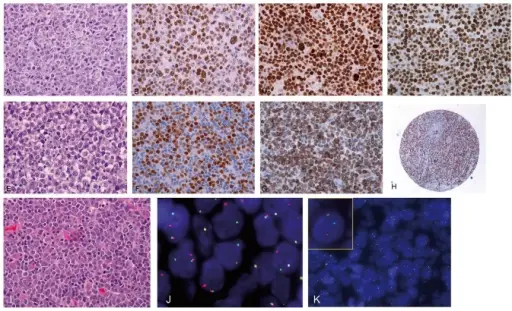
-Histology: The histology associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma shows a relatively large cell size usually 4-5 times the diameter of a small lymphocyte and a diffuse pattern of growth. Tumor cells have a round or oval nucleus that appears vesicular due to margination of chromatin to the nuclear membrane. Cytoplasm is moderately abundant and may be pale or basophilic.
How does Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Present?
Patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma typically present with a slight male predominance and the median patient age is about 60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma typically include a rapidly enlarging mass at a nodal or extranodal site. The Waldeyer ring, oropharyngeal lymphoid tissue that includes the tonsils and adenoids, is involved most commonly. Involvement of the liver and spleen may take the form of a large destructive masses.
How is Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is diagnosed mainly through biopsy of an enlarged lymph node and examining it through a microscope.
How is Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Treated?
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is treated with intensive combination chemotherapy. Adjuvant therapy with anti-CD20 improves both the initial response and overall outcome.
What is the Prognosis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma?
The prognosis of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma is fair with remission rate of 60-80% and a cure rate of 40-50% when treated with intensive chemotherapy. DLBCLs are aggressive tumors that are rapidly fatal without treatment.