DNA methylation results in methyl groups being added to the DNA molecules at C5 position of cytosine to make it 5-methylcytosine. DNA methylation regulates gene expression by inhibiting the binding of transcription factors to DNA.
What is DNA Methylation?
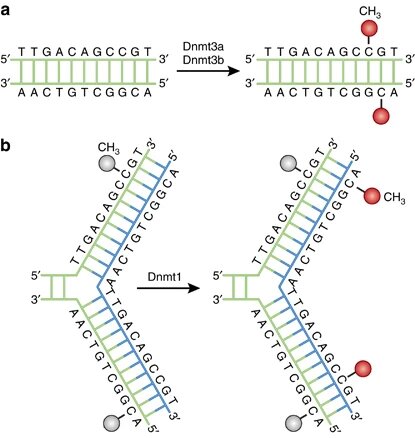
DNA methylation pathways. A family of DNA methyltransferases (Dnmts) catalyzes the transfer of a methyl group from S-adenyl methionine (SAM) to the fifth carbon of cytosine residue to form 5-methylcytosine (5mC). (a) Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b are the de novo Dnmts and transfer methyl groups (red) onto naked DNA. (b) Dnmt1 is the maintenance Dnmt and maintains DNA methylation pattern during replication. When DNA undergoes semiconservative replication, the parental DNA stand retains the original DNA methylation pattern (gray). Dnmt1 associates at the replication foci and precisely replicates the original DNA methylation pattern by adding methyl groups (red) onto the newly formed daughter strand (blue). Not altered. CC.
DNA Methylation and Its Basic Function
Lisa D Moore, Thuc Le & Guoping Fan