Down syndrome is a chromosomal disorder (trisomy 21) that results in mental retardation.
What is Down Syndrome?
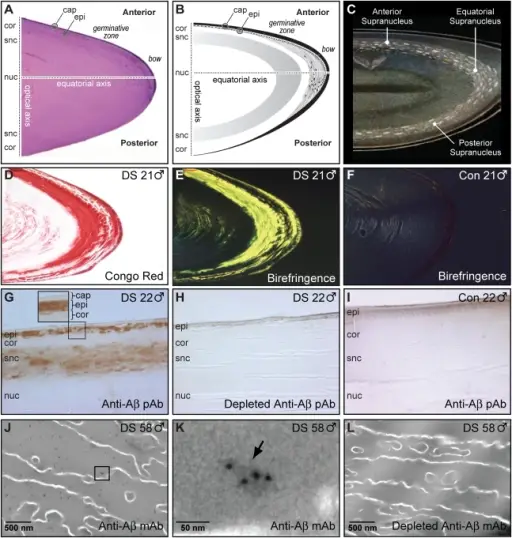

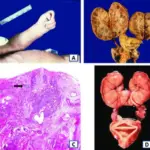
(A) Histological section of a human lens obtained from a 21-year-old male subject with Down syndrome. Hematoxylin and eosin. (B) Schematic diagram identifying anatomical regions of the human lens (C) Archival rendering of classical coronary cerulean “flake” arcuate cataracts in a 40-year-old male with presumptive Down syndrome. This historical folio drawing illustrates the mature Down syndrome supranuclear cataract phenotype with dominant subequatorial localization and anteroposterior extension. (D-F) Congo red amyloid histochemical analysis of lenses from a 21-year-old male with Down syndrome and age-matched normal male control. (D) Congophilia in the cortex and supranuclear subregion of the lens from a 21-year-old male with Down syndrome. (E) Intense co-localizing apple-green birefringence in the corresponding cortical and supranuclear subregions of the same Congo red-stained Down syndrome lens imaged with cross-polarized illumination. (F) Amyloid histochemical analysis of a lens from a 21-year-old normal control subject did not demonstrate Congophilia nor classical apple-green birefringence under identical cross-polarized illumination. (G) Aβ immunoreactivity in the epithelium, deep cortex, and supranuclear regions in a lens from a 22-year-old male with Down syndrome. Inset, magnified detail of the anterior lens (box) (H) Confirmation of anti-Aβ antibody specificity in the same Down syndrome lens by immunodepletion of the detection antibody with synthetic human Aβ (I) Absence of Aβ immunoreactivity in the lens of a normal 22-year-old male control subject. (J) Heterogeneously distributed anti-Aβ immunoreactive protein aggregates of dimensions ∼5–200 nm localize heterogeneously within the lens fiber cell cytoplasm. Aβ immunoreactivity was not detected at the plasmalemma (K) High-magnification electron micrograph of a single Aβ-immunoreactive cytoplasmic protein aggregate (arrow). Multiple immunogold particles detect a single cytoplasmic protein aggregate with the longest axial cross-section ∼50 nm (L) Confirmation of anti-Aβ antibody specificity. Anti-Aβ immunostaining was not detected in Down syndrome lens when probed with immunodepleted anti-Aβ antibody. Alzheimer's disease amyloid-beta links lens and brain pathology in Down syndrome: Moncaster JA, Pineda R, Moir RD, Lu S, Burton MA, Ghosh JG, Ericsson M, Soscia SJ, Mocofanescu A, Folkerth RD, Robb RM, Kuszak JR, Clark JI, Tanzi RE, Hunter DG, Goldstein LE - PloS one (2010). Not altered. CC.