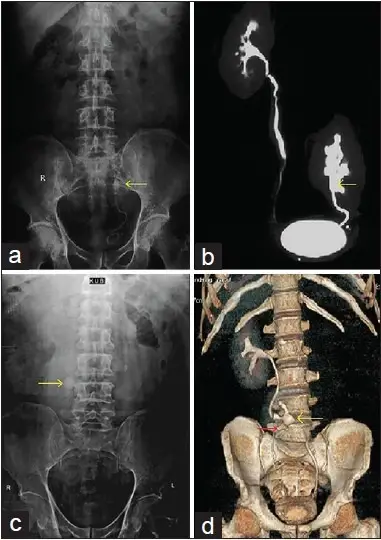
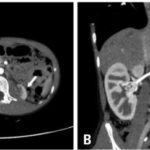
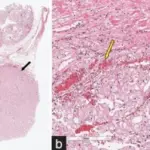
Ectopic kidney is the kidney that is not located in its normal anatomic position.
What is the Pathology of Ectopic Kidney?
The pathology of ectopic kidney is:
-Etiology: The cause of ectopic kidney is idiopathic, congenital factors.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ectopic kidney is not well understood.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with an ectopic kidney shows a normal or small sized kidney in an unusual position.
-Histology: Glomeruli and or tubules.
How does Ectopic Kidney Present?
Patients with ectopic kidney typically have no gender prevalence reported present at the age range of prenatal to adulthood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ectopic kidney include; asymptomatic, urine retention, urinary frequency, frequent UTI, kidney stones, abdomen lump or mass, blood pressure.
How is Ectopic Kidney Diagnosed?
Ectopic kidney is diagnosed through lab work- Kidney function test. Imaging- prenatal ultrasound, MRI, x-ray.
How is Ectopic Kidney Treated?
Ectopic kidney is treated through symptomatic and supportive care.
What is the Prognosis of Ectopic Kidney?
The prognosis of ectopic kidney is good.