Ectopic pancreas is a condition in which pancreatic tissues are found in places other than the normal anatomical position.
What is the Pathology of Ectopic Pancreas?
The pathology of ectopic pancreas is:
-Etiology: The cause of ectopic pancreas is abnormal embryologic development.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to ectopic pancreas is persistence of a duodenal evagination intricated in the typical growth of the pancreas. The remnant travels with the developing gastrointestinal tract resulting in its numerous locations.
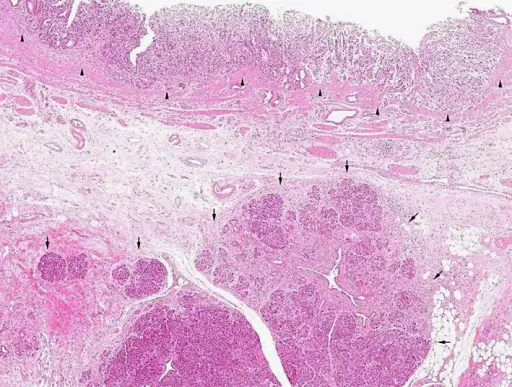
-Morphology: The morphology associated with ectopic pancreas shows existence of a characteristic central ductal orifice.
-Histology: The histology associated with ectopic pancreas shows the presence of islets of Langerhans, pancreatic acini.
How does Ectopic Pancreas Present?
Patients with ectopic pancreas are usually males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with ectopic pancreas include sessile mass, may cause pain from localized inflammation, or, rarely, may incite mucosal bleeding, anemia, melena abdominal fullness, and nausea.
How is Ectopic Pancreas Diagnosed?
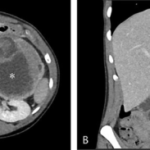
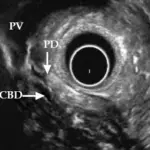
Ectopic pancreas is diagnosed through radiological study (Endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS ) and clinical presentations.
How is Ectopic Pancreas Treated?
Ectopic pancreas is treated through surgical interventions laparoscopic wedge resection.
What is the Prognosis of Ectopic Pancreas?
The prognosis of ectopic pancreas is good, with proper management.