Embryonal carcinoma is a germ cell neoplasm categorized with primitive epithelial cells with patent pleomorphism and several histologic patterns.
What is the Pathology of Embryonal Carcinoma?
The pathology of embryonal carcinoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of embryonal carcinoma is genetic, environmental factors, and idiopathic.
-Genes involved: embryonal carcinoma-specific gene DNMT3B.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to embryonal carcinoma unknown.
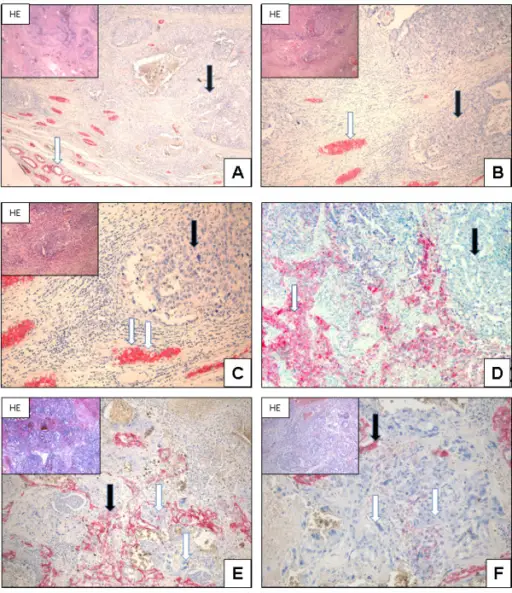
-Morphology: The morphology associated with embryonal carcinoma shows smaller tumor does not replace the whole testis, mass pied, are poorly demarcated at the margins, and scattered by hemorrhage and necrosis.
-Histology: The histology associated with embryonal carcinoma shows basally located nuclei and apical cytoplasm in teratomas, epithelial appearance, and are large and anaplastic neoplastic cells.
How does Embryonal Carcinoma Present?
Patients with embryonal carcinoma are typically males between 20 to 30 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with embryonal carcinoma include a painless palpable mass on the testis.
How is Embryonal Carcinoma Diagnosed?
Embryonal carcinoma is diagnosed through imaging studies, and biopsy.
How is Embryonal Carcinoma Treated?
Embryonal carcinoma is treated through surgical interventions and chemotherapy.
What is the Prognosis of Embryonal Carcinoma?
The prognosis of embryonal carcinoma is fair.