Epithelial or follicular inclusion cyst (Wen) is a type of non-cancerous growth that occurs on parts of the skin with minimal hair and occurs as a result of the epidermis embedding itself into the dermis.
What is the Pathology of Follicular Inclusion Cyst?
The pathology of follicular inclusion cyst is: the study of the conditions of the skin mostly the squamous epithelium and outlining the histology and the pathology of the disease.
-Etiology: The cause of follicular inclusion cyst include trauma, infection, or blockage leading to misplacement of the epidermis.
-Genes involved: None.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to follicular inclusion cyst occurs as a result of the increased production of the epidermal cells in the location of the dermis.
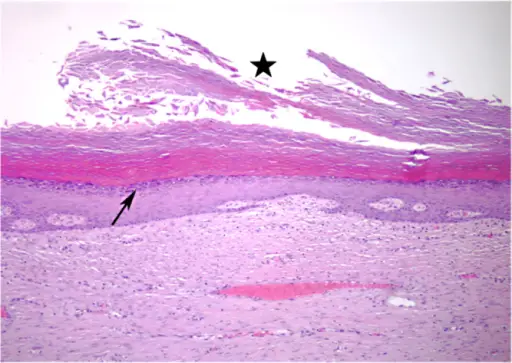
-Morphology: The morphology associated with follicular inclusion cyst shows dome-shaped lumps filled with keratin, mobile, and a size ranging from 0.5 cm.
-Histology: The histology associated with follicular inclusion cyst shows a thin layer of squamous epithelium.
How does Follicular Inclusion Cyst Present?
Patients with follicular inclusion cysts are typically more common in males than females, present at an age range of 20-60 years. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with follicular inclusion cyst include small round swelling under the skin, redness, and tenderness if infected, thick foul-smelling yellow discharge may be seen.
How is Follicular Inclusion Cyst Diagnosed?
The follicular inclusion cyst is diagnosed palpation, physical examination, and needle biopsy.
How is Follicular Inclusion Cyst Treated?
The follicular inclusion cyst is treated by incision and drainage of the cyst to remove the contents inside and also to some extent there is the injection of steroid medication.
What is the Prognosis of Follicular Inclusion Cyst?
The prognosis of follicular inclusion cyst is good.