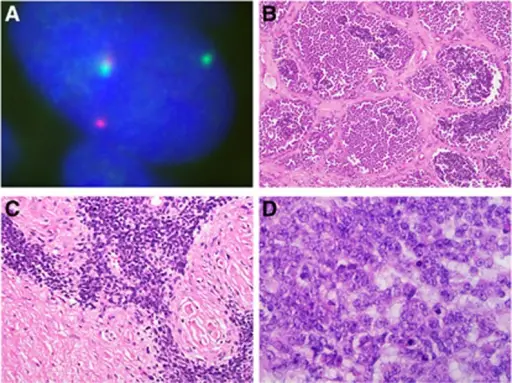
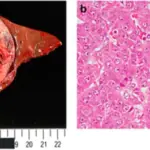
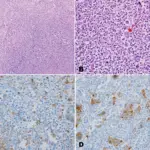
Ewing sarcoma is a type of tumor that forms in bone or soft tissue and may be found in the bones of the legs, arms, feet, hands, chest, pelvis, spine, or skull.
What is the Pathology of Ewing Sarcoma?
The pathology of Ewing sarcoma is:
–Etiology: The cause of Ewing sarcoma is: It’s not inherited, but it can be related to non-inherited changes in specific genes during a person’s lifetime. When chromosomes 11 and 22 exchange genetic material, it activates an overgrowth of cells. This may lead to the development of Ewing’s sarcoma.
–Genes involved: Translocation of EWSR1 gene on chromosome 22 and the FLI1 gene on chromosome 11.
–Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Ewing sarcoma involves the EWS/FLI protein has the DNA-binding function of the FLI protein as well as the transcription regulation function of the EWS protein. It is thought that the EWS/FLI protein turns the transcription of a variety of genes on and off abnormally. This dysregulation of transcription leads to uncontrolled growth and division and abnormal maturation and survival of cells, causing tumor development.
–Morphologic changes: The morphologic changes involved with Ewing sarcoma are small round blue cells.
How does Ewing Sarcoma Present?
Patients with Ewing sarcoma are typically males between ages of 10 to 20 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Ewing sarcoma include pain, swelling, fever, weight loss, and potentially paralysis if the tumor is in the spinal region.
How is Ewing Sarcoma Diagnosed?
Ewing sarcoma is diagnosed by CT scan, X-rays, ultrasound, MRI, and biopsy.
How is Ewing Sarcoma Treated?
Ewing sarcoma is treated by surgery, radiotherapy, or chemotherapy
What is the Prognosis of Ewing Sarcoma?
The prognosis of Ewing sarcoma is good. About 70 percent of children with Ewing sarcoma are cured. Teens aged 15 to 19 have a lower survival rate of about 56 percent. For children diagnosed after their disease has spread, the survival rate is less than 30 percent.