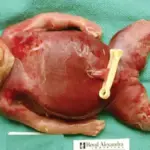
Fetal hydrops is the accumulation of edematous fluid in the fetus during intrauterine growth.
What is the Pathology of Fetal Hydrops?
The pathology of fetal hydrops is:
–Etiology: The cause of fetal hydrops is an imbalance of interstitial fluid production and lymphatic return. Fluid accumulation in the fetus can result from obstructed lymphatic flow, congestive heart failure, or decreased plasma osmotic pressure.
-Genes involved: Rh incompatibility
–Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to fetal hydrops are when the rate of interstitial fluid production by capillary ultrafiltration exceeds the rate of interstitial fluid return to the lymphatic circulation. Developmental differences in the microcirculation and lymphatic system of the fetus, as compared with mature subjects, renders the fetus susceptible to interstitial fluid accumulation.
–Morphologic changes: The morphological changes involved with fetal hydrops are the presence of 2 or more abnormal fluid collections in the fetus. These include ascites, pleural effusions, pericardial effusion, and generalized skin edema.
How does Fetal Hydrops Present?
Fetal hydrops does not have gender differences. Patients wit hfetal hydrops typically present 12 to 20 weeks gestation. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with fetal hydrops include thickened placenta, large amounts of amniotic fluid, enlarged liver, enlarged spleen, enlarged heart in the baby, fluid buildup in the baby’s abdomen. Symptoms after birth are severe swelling, splenomegaly, hepatomegaly, and difficulty breathing.
How is Fetal Hydrops Diagnosed?
Fetal hydrops can be diagnosed during pregnancy or after the baby is born with ultrasound, blood tests, or amniocentesis.
How is Fetal Hydrops Treated?
Fetal hydrops treatment during pregnancy is treatable only in certain situations. After birth, fetal hydrops treatment may include: respiratory support for difficulty breathing, removal of excessive fluid from spaces around the lungs and abdomen using a needle, and diuretic medications to help the kidneys remove excess fluid. Red blood cell transfusions may also be indicated.
What is the Prognosis of Fetal Hydrops?
The prognosis of fetal hydrops is poor. Fetal hydrops can be fatal. The earlier in the pregnancy that fetal hydrops is identified, the worse the prognosis is.