A fibroadenoma is a benign biphasic tumor composed of both glandular epithelial and stromal components of the terminal duct lobular unit.
What is the Pathology of Fibroadenoma?
The pathology of fibroadenoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of fibroadenoma is associated with cyclosporine immunosuppression.
-Genes involved: MED12 exon 2 mutations.
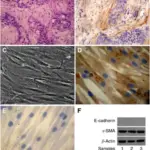
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to fibroadenoma isn’t completely understood. Myxoid fibroadenoma is associated with Carney complex.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with fibroadenoma shows a palpable breast mass.
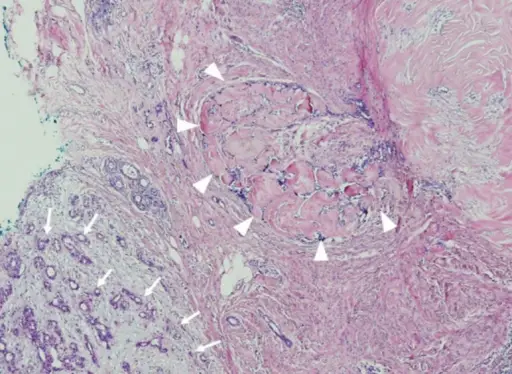
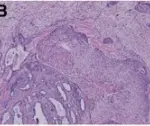
-Histology: The histology associated with fibroadenoma shows well circumscribed, unencapsulated, biphasic tumor, and proliferation of both glandular and stromal elements.
How does Fibroadenoma Present?
Patients with fibroadenoma typically are younger females with palpable breast masses.
How is Fibroadenoma Diagnosed?
Fibroadenoma is diagnosed by biopsy and histologic examination of involved tissue.
How is Fibroadenoma Treated?
Fibroadenoma is treated depending on patient’s risk factors and patient’s preference.
What is the Prognosis of Fibroadenoma?
The prognosis of fibroadenoma is good.