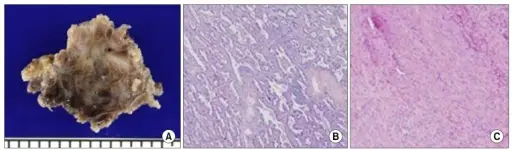
Fibromatosis is the low grade’s infiltrative spindle cell neoplasm composed of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts.
What is the Pathology of Fibromatosis?
The pathology of fibromatosis is:
-Etiology: The cause of fibromatosis may include surgery or trauma.
-Genes involved: CTNNB1 mutation or inactivating APC mutation
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to fibromatosis is through the WNT or beta catenin pathway these mutations motivate cells to proliferate while destabilizing beta catenin that then accumulates within the nucleus.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with fibromatosis shows a palpable breast mass.
-Histology: The histology associated with fibromatosis shows long intersecting fascicles composed of bland spindle cells with indistinct borders, hyperchromatic nuclei with occasional nucleoli, and eosinophilic cytoplasm.
How does Fibromatosis Present?
Patients with fibromatosis typically females with a complaint of a slow growing breast mass.
How is Fibromatosis Diagnosed?
Fibromatosis is diagnosed through mammography.
How is Fibromatosis Treated?
Fibromatosis is treated by surgical local excision.
What is the Prognosis of Fibromatosis?
The prognosis of fibromatosis is fair.