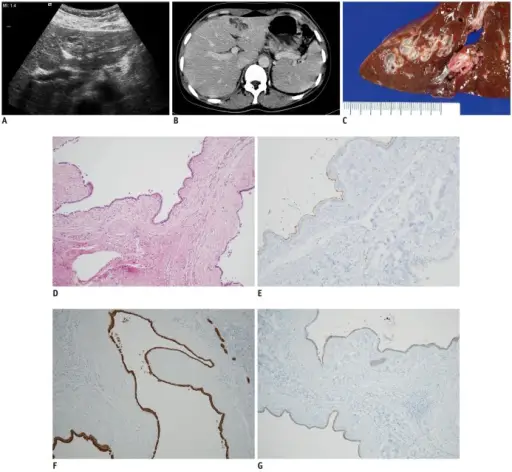
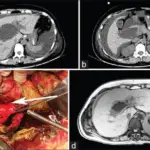
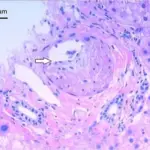
Fibropolycystic disease is the collective term for a group of congenital liver and biliary abnormalities resulting from abnormal development of the ductal plates.
What is the Pathology of Fibropolycystic Disease?
The pathology of fibropolycystic disease is:
-Etiology: The cause of fibropolycystic disease is unknown, however, it is believed that estrogen is the main cause.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to fibropolycystic disease includes abnormal development of the embryonic ductal plates.
-Histology: The histology associated with fibropolycystic disease shows periportal fibrosis and irregularly shaped proliferating bile ducts.
How does Fibropolycystic Disease Present?
Patients with fibropolycystic disease typically affect females present at the age range of 25-45. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with fibropolycystic disease include vauge abdominal symptoms.
How is Fibropolycystic Disease Diagnosed?
Fibropolycystic disease is diagnosed through a mammogram, ultrasound, and MRIs.
How is Fibropolycystic Disease Treated?
Fibropolycystic disease is treated with surgical excision and over-the-counter medications.
What is the Prognosis of Fibropolycystic Disease?
The prognosis of fibropolycystic disease is good if treated timely.