Follicular lymphoma is the most common form of indolent non-hodgkin lymphoma in the United States affecting 15,000 to 20,000 individuals per year.
What is the Pathology of Follicular Lymphoma?
The pathology of follicular lymphoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of follicular lymphoma is multifactorial.
-Genes involved: KMT2D gene.
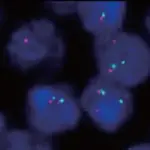
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to follicular lymphoma involve chromosomal translocations involving BCL2. Its hallmark is a 14;18 translocation that juxtaposes IGH locus on chromosome 14 and the BCL2 locus on chromosome 18.
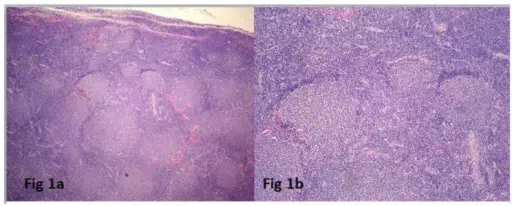
-Histology: The histology associated with follicular lymphoma shows a nodular and diffuse growth pattern in involved lymph nodes. Two cell types are present: 1) small cells with irregular or cleaved nuclear contours and scant cytoplasm, which are known as centrocytes; and 2) larger cells with open nuclear chromatin, several nucleoli and modest amounts of cytoplasm referred to as centroblasts.
How does Follicular Lymphoma Present?
Patients with follicular lymphoma typically present in middle ages and afflicts males and females equally. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with follicular lymphoma include painless, generalized lymphadenopathy. It usually follows an indolent waxing and waning course.
How is Follicular Lymphoma Diagnosed?
Follicular Lymphoma is diagnosed through histology, specifically a biopsy of an affected lymph node. Immunophenotyping may also be done. Neoplastic cells resemble normal germinal centers CD19,CD20,CD10, surface Immunoglobulin and BCL6. Most cases are BCL2 positive.
How is Follicular Lymphoma Treated?
Follicular lymphoma is treated with low-dose chemotherapy or immunotherapy (anti-CD20 antibody). It is also responsive to BTK inhibitors and BCL2 inhibitors.
What is the Prognosis of Follicular Lymphoma?
The prognosis of follicular lymphoma is fair with a median survival of 7 to 9 years. Histologic transformation into diffuse large B-cell lymphoma occurs in 30-50% of patients leading to a median survival of less than 1 year.