Fragile X syndrome is a genetic condition that causes intellectual disability, and a range of developmental problems.
What is Fragile X Syndrome?
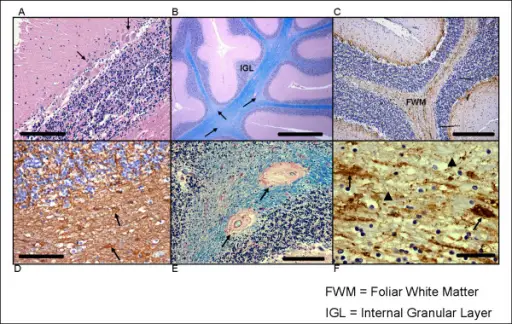
(A) Decreased numbers of Purkinje cells (PCs) and clusters of PCs (arrows) in which cells are often misoriented. Haematoxylin and eosin, original magnification ×200; scale bar = 200 μm. (B) The patchy pallor of foliar white matter and increased variability in the thickness of the internal granular cell layer (IGL). Arrows indicate foci of myelin pallor. Luxol fast blue-periodic-acid-Schiff (LFB-PAS), original magnification ×200; scale bar = 1 mm. (C) Diffuse axonal loss in cerebellar foliar white matter (FWM) (neurofilament immunohistochemistry, original magnification ×100; scale bar = 400 μm); (D) Activated astrocytes in foliar white matter, a finding not seen in deep cerebellar white matter. Arrows indicate abnormal astrocytes. (glial fibrillary acidic protein immunohistochemistry, original magnification ×200; scale bar = 200 μm). (E) Vascular hyalinosis within foliar white matter, as indicated by arrows. LFB-PAS, original magnification ×200; scale bar = 200 μm. (F) High magnification of foliar white matter axonal abnormalities that include axonal loss (arrowheads) and swollen axons, as indicated by arrows. Neuropathologic features in the hippocampus and cerebellum of three older men with fragile X syndrome: Greco CM, Navarro CS, Hunsaker MR, Maezawa I, Shuler JF, Tassone F, Delany M, Au JW, Berman RF, Jin LW, Schumann C, Hagerman PJ, Hagerman RJ - Molecular autism (2011). Not altered. CC.