Gigantism is an abnormality in which while the epiphyseal growth plates are open at 25 years and below, an oddly high linear growth occurs owing to the extreme action of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I).
What is the Pathology of Gigantism?
The pathology of gigantism is:
-Etiology: The cause of gigantism is the pituitary gland adenoma, excessive growth hormone.
-Genes involved: GPR101, Familial isolated pituitary adenoma (FIPA), PRKAR1A, GNAS, MEN1, CDKN1B, McCune-Albright syndrome (MAS),
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to gigantism is the result of primary GH surplus, augmented GHRH production, and undue secretion of IGF-binding protein. Elevated tissue levels of free IGF-I, arbitrate most, of the growth-related consequences in gigantism.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with gigantism shows Increased stature
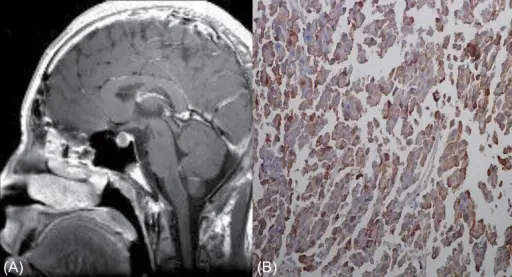
-Histology: The histology associated with gigantism shows sparsely/ densely granulated, Somatotrope carcinoma, Mixed somatotrope-lactotroph adenoma, infiltration of glycosaminoglycans, edematous and myxoid, slightly increased number of fibroblasts, and thinning of the epidermis.
How does Gigantism Present?
Patients with gigantism typically have equal prevalence in males and females present at an age range of 25 years and below. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with gigantism include Endocrinopathies, visual changes in tall stature, headaches, macrocephaly, coarse facial structures, hyperhidrosis, osteoarthritis, cardiovascular disease, and tumors.
How is Gigantism Diagnosed?
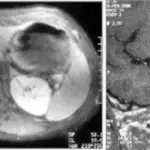
Gigantism is diagnosed through laboratory studies to detect excess growth hormones, oral glucose tests, IGF elevated. Imaging; MRI for pituitary adenomas, CT scan evaluate the adrenal, pancreatic, ovarian tumors producing GH/GHRH.
How is Gigantism Treated?
Gigantism is treated through medical care; dopamine and somatostatin analog, radiation therapy. Transsphenoidal surgery for adenoma removal may be needed.
What is the Prognosis of Gigantism?
The prognosis of gigantism is because an insignificant number of people with the condition, rates of mortality and morbidity throughout childhood are unidentified.