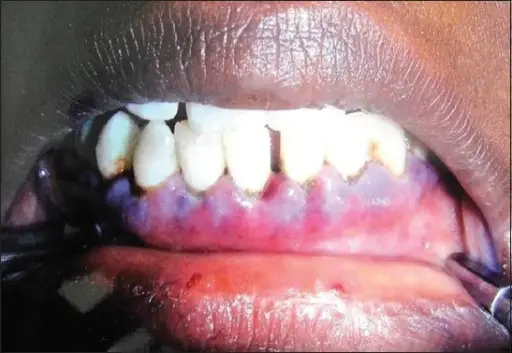
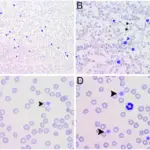
Glanzmann thrombasthenia is a bleeding disorder.
What is the Pathology of Glanzmann Thrombasthenia?
The pathology of Glanzmann thrombasthenia is:
-Etiology: The cause of Glanzmann thrombasthenia is the lack of a protein that is normally on the surface of platelets and is needed for platelets to clump together to form blood clots.
-Genes involved: ITGA2B and ITGB3.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to Glanzmann thrombasthenia is the platelet integrin GPIIb/IIIa abnormality that results in platelets not aggregating when they need to.
How does Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Present?
Patients with Glanzmann thrombasthenia typically are males or females present at the age range of infants. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with Glanzmann thrombasthenia include easy bleeding, and nose bleeds.
How is Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Diagnosed?
Glanzmann thrombasthenia is diagnosed with platelet function analysis (PFA), prothrombin time (PT), and partial thromboplastin time (PTT).
How is Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Treated?
Glanzmann Thrombasthenia is treated with platelet transfusions as needed.
What is the Prognosis of Glanzmann Thrombasthenia?
The prognosis of Glanzmann thrombasthenia is fair.