Glanzmann thrombasthenia is an erratic platelet ailment characterized by plate.lets that have qualitative/quantitative shortages of the fibrinogen receptor αIIbβ3.
What is the Pathology of Glanzmann Thrombasthenia?
The pathology of glanzmann thrombasthenia is:
-Etiology: The cause of glanzmann thrombasthenia is genetic factors.
-Genes involved: ITGA2B or ITGB3 genes.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to glanzmann thrombasthenia results from thrombasthenic platelets failing to aggregate in retort to ADP, epinephrine, collagen, or thrombin due to deficit or disfunction of glycoprotein IIb-IIIa, required in the establishment of bonds amid platelets thru binding fibrinogen and vWF.
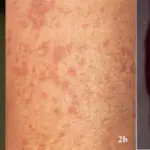
-Morphology: Rashes.
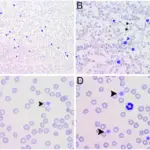
-Histology: Red blood cell changes.
How does Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Present?
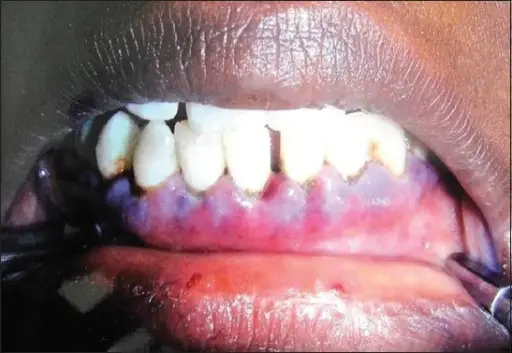
Patients with Glanzmann thrombasthenia typically have a female predominance present at age range of childhood. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with glanzmann thrombasthenia include mucosal haemorrhage, gingival haemorrhage, petechiae and ecchymoses, menorrhagia, and gastrointestinal haemorrhage.
How is Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Diagnosed?
Glanzmann thrombasthenia is diagnosed through laboratory evaluation such as prothrombin time, complete blood cell count, activated partial thromboplastin time, monoclonal antibodies test, and flow cytometry.
How is Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Treated?
Glanzmann thrombasthenia is treated preventive measures, avoidance of antiplatelet agents, and platelet transfusion.
What is the Prognosis of Glanzmann Thrombasthenia?
The prognosis of glanzmann thrombasthenia is good with appropriate supportive care.