Gonadoblastoma is a rare neoplasm comprising a blend of gonadal stromal and germ cells elements, that arise in dysgenetic gonads.
What is the Pathology of Gonadoblastoma?
The pathology of gonadoblastoma is:
-Etiology: The cause of gonadoblastoma is dysgenetic gonads, undescended testis, and genetic mutations.
-Genes: Testis-specific protein Y-encoded (TSPY).
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to gonadoblastoma include dysgenesisthat results in germinal factor.
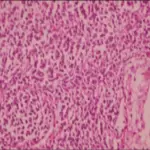
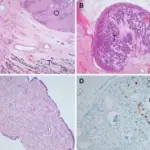
-Morphology: The morphology associated with gonadoblastoma shows the variable size, yellowish-white and soft.
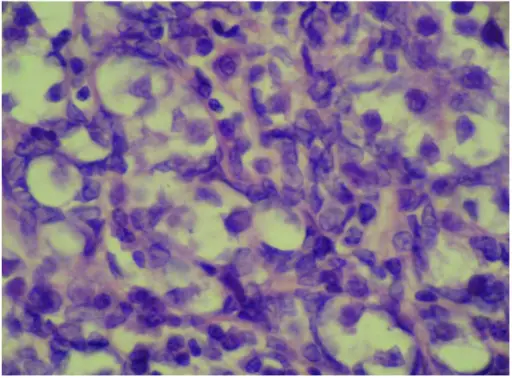
-Histology: The histology associated with gonadoblastoma shows two principal cell types large germ cells resembling seminoma cells, and small cells resembling immature sertoli, leydig, and granulosa cells.
How does Gonadoblastoma Present?
Patients with gonadoblastoma are typically young males. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with gonadoblastoma include the history of the atypical genitourinary structure, palpable abdominal mass, and undescended testis.
How is Gonadoblastoma Diagnosed?
Gonadoblastoma is diagnosed through serum electrolyte panel, endocrinologic evaluation, biopsy, and chromosome analysis.
How is Gonadoblastoma Treated?
Gonadoblastoma is treated through surgical interventions.
What is the Prognosis of Gonadoblastoma?
The prognosis of gonadoblastoma is good if the lesion is removed before the alteration to a malignant type.