Granulomatosis with polyangiitis is also known as Wegener’s granulomatosis a condition that causes inflammation of the blood vessels falling under necrotizing vasculitis.
What is the Pathology of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis?
The pathology of granulomatosis with polyangiitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of granulomatosis with polyangiitis presence of immunocomplexes circulating in the bloodstream.
-Genes involved: the presence of the HLA-DPB1 gene.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to granulomatosis with polyangiitis is a result of ANCA induced leukocyte activation in which the cytokines and the metabolites of lipids are produced this, in turn, leads to inflammation and formation of necrosis of the blood vessels wall.
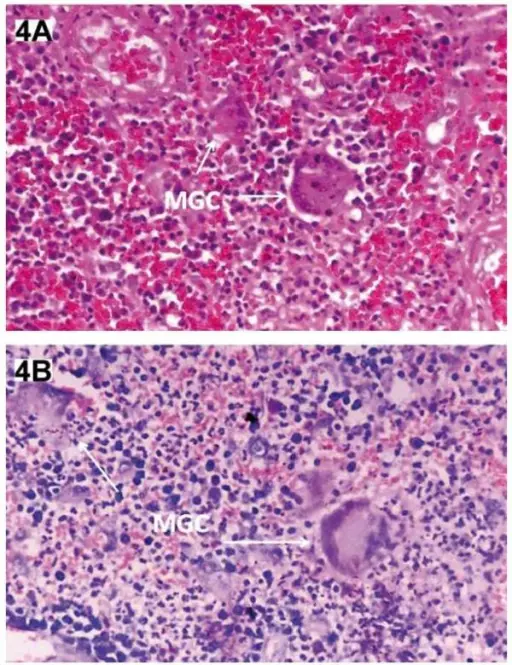
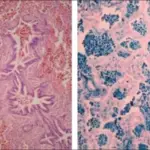
-Histology: The histology associated with granulomatosis with polyangiitis shows necrotic fibrinoid granulomas which are extensively infiltrated by neutrophils and mononuclear cells, giant cells of foreign bodies are also seen.
How does Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Present?
Patients with granulomatosis with polyangiitis typically are male. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with polyangiitis with Granulomatosis hearing loss and blood in urine sinus pain, joint pain, fever, cough.
How is Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Diagnosed?
The granulomatosis with polyangiitis is diagnosed through physical examination followed by a couple of lab-works tom check for any antibodies in the circulating system.
How is Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis Treated?
Granulomatosis with polyangiitis is treated mostly depending on the severity of the disease. Medication includes steroids, immunosuppressors, antibiotics, and also antibodies. Other options are palliative care and hemodialysis if it affects the kidneys.
What is the Prognosis of Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis?
The prognosis of granulomatosis with polyangiitis is good with a survival rate of 80%.