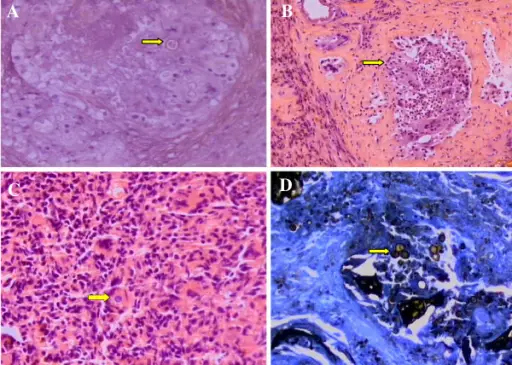
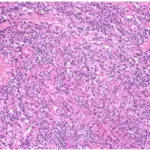
Granulomatous prostatitis is an inflammatory ailment of the prostate having granulomas presence as histologic features.
What is the Pathology of Granulomatous Prostatitis?
The pathology of granulomatous prostatitis is:
-Etiology: The cause of granulomatous prostatitis is microbes such as fungi bacteria, viruses, and parasites. obstruction to prostatic ducts and stillness of secretions, or BCG for treatment of bladder cancer.
-Genes involved: Unknown.
-Pathogenesis: The sequence of events that lead to granulomatous prostatitis, blockage ducts, and stillness of secretions results in epithelial distraction leading to the seepage of bacterial toxins, cellular debris, and prostatic secretions, such as corpora amylacea, and semen, to the stroma.
-Morphology: The morphology associated with granulomatous prostatitis shows firm to the hard gland.
-Histology: The histology associated with granulomatous prostatitis shows the presence of macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and some multinucleate giant cells.
How does Granulomatous Prostatitis Present?
Patients with granulomatous prostatitis are typically males within the age range of 18 to 86 years old. The symptoms, features, and clinical findings associated with granulomatous prostatitis include a history of UTI, urinary frequency, TB infection, mild hematuria, and fever.
How is Granulomatous Prostatitis Diagnosed?
Granulomatous prostatitis is diagnosed through history and physical examination.
How is Granulomatous Prostatitis Treated?
Granulomatous prostatitis is treated through mainly supportive, temporary catheterization hot sitz baths, and fluids therapy. Treatment of concurrent infection when indicated.